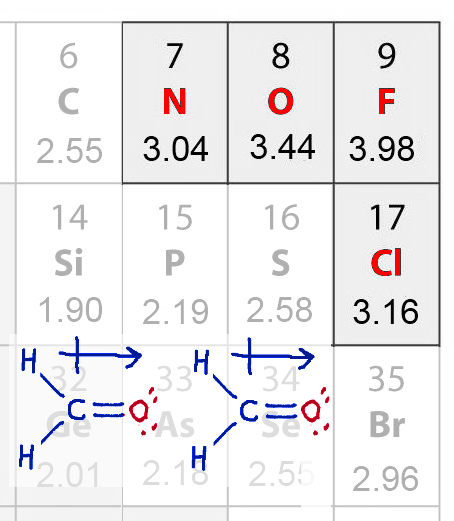
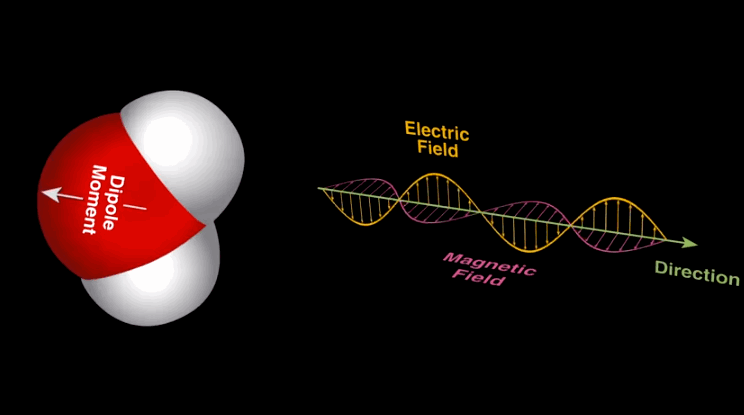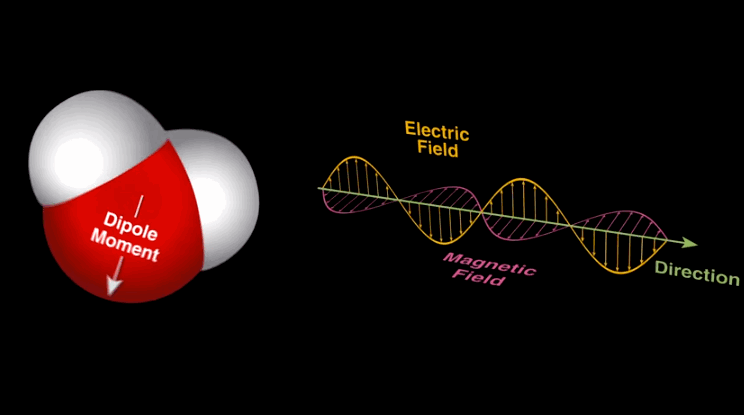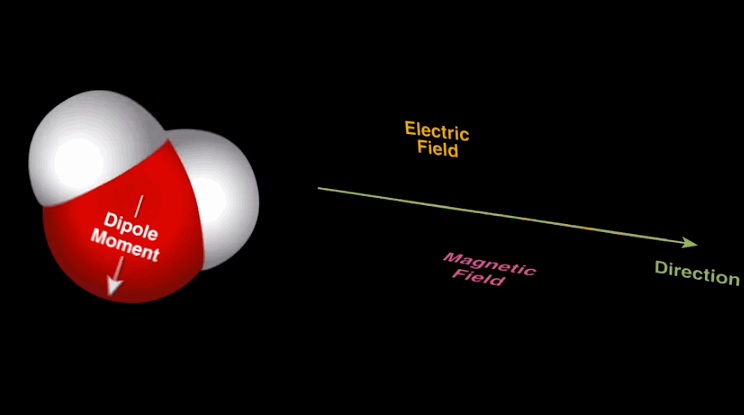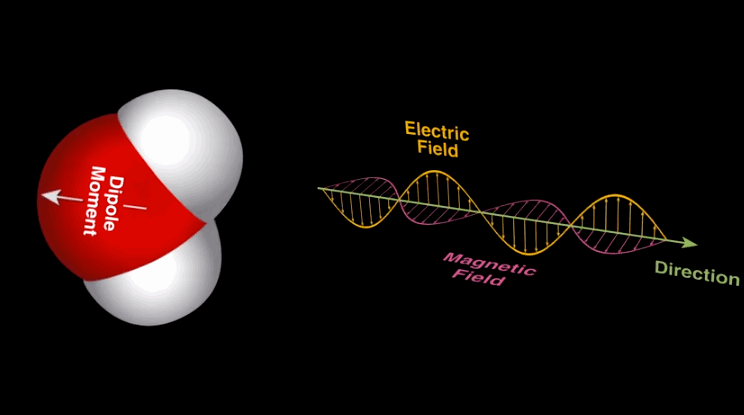
Dipole-dipole
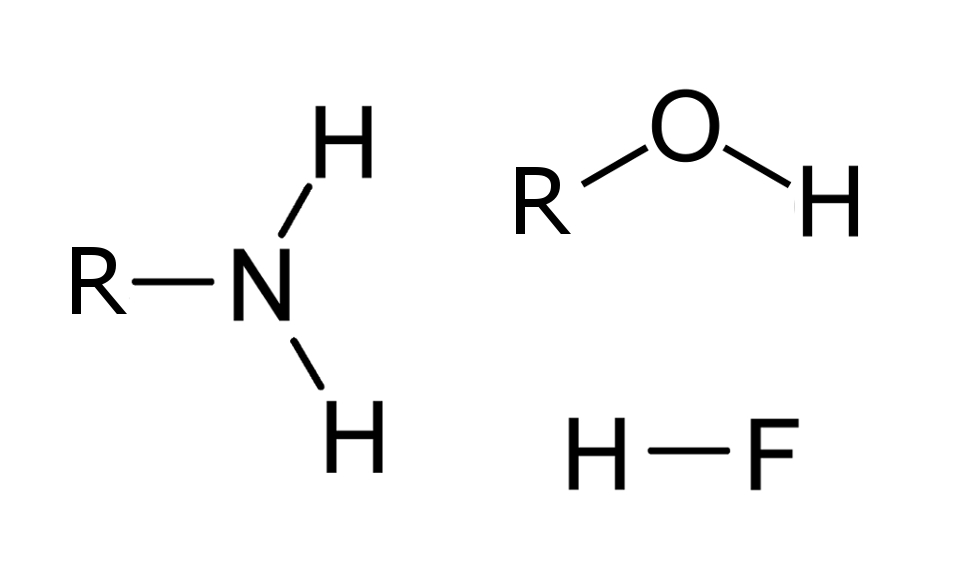
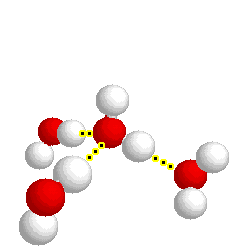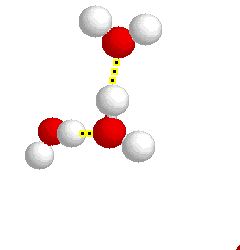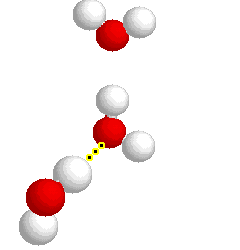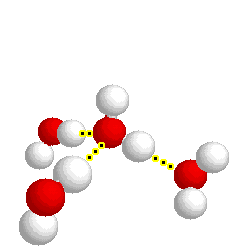
H-bonding
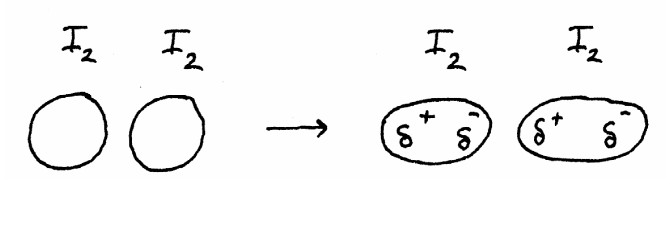

Intermolecular forces: ReviewMain intermolecular forcesWater soluble compound (more complex)Water soluble compound (biomolecule)Boiling pointfreezing pointvitamin B-12 |


Dipole-dipole |


H-bonding |


London dispersion |
|
Compound |
dipole-dipole |
H-bonding |
London dispersion forces |
|
a) |
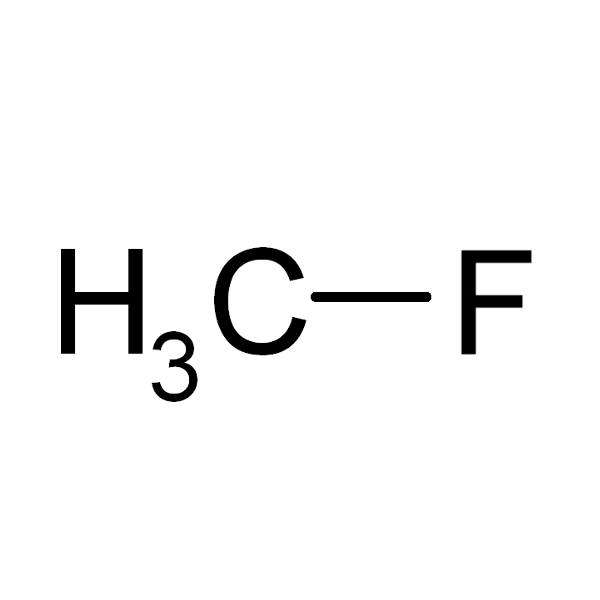
CH3 – F |
 |
 |
 |
b) |
CH3 – CH3 |
 |
 |
 |
c) |
|
 |
 |
 |
d) |
H – O – H |
 |
 |
 |
e) |
CH3 – O – CH3 |
 |
 |
 |
f) |
H – C ≡ N |
 |
 |
 |
Compound |
dipole-dipole |
H-bonding |
London dispersion forces |
|
a) |
CH3 – F |
 |
 |
 |
b) |
CH3 – CH3 |
 |
 |
 |
c) |
|
 |
 |
 |
d) |
H – O – H |
 |
 |
 |
e) |
CH3 – O – CH3 |
 |
 |
 |
f) |
H – C ≡ N |
 |
 |
 |
O = C = O(a) |
S = C = O(b) |
H – N = CH – NH2(c) |
O = S = O(d) |
SiCl4(e) |
H – I(f) |
|
S = C = Owater soluble (dipole) |
H – N = C – NH2water soluble (H-bonding) |
O = S = Owater soluble (bent - dipole) |
|
H – Iwater soluble (acid) |
 |
 |
 |
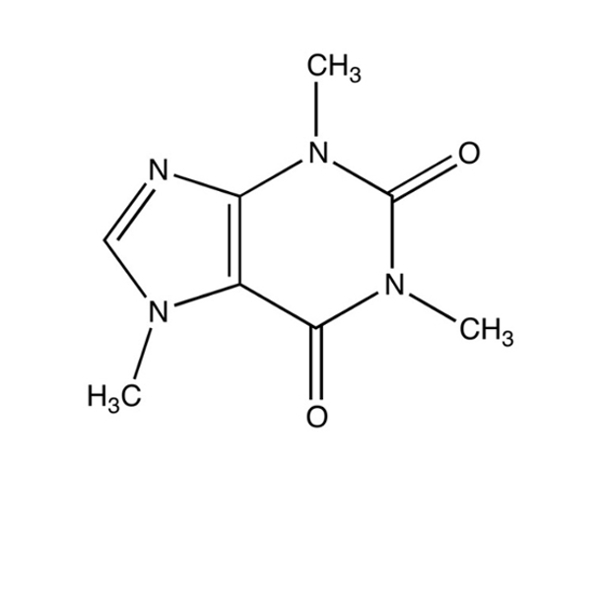
A |
B |
C |
 |
 |
 |
|
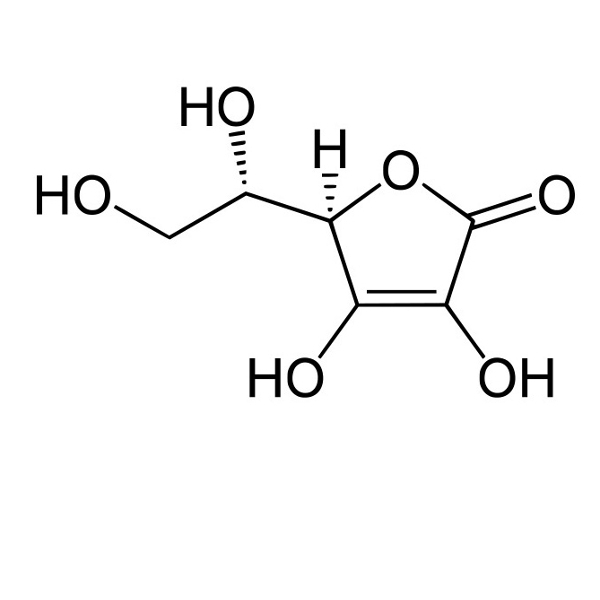
partially soluble: 2 g/100 mL |
Vitamin-C: water soluble |
 |
 |
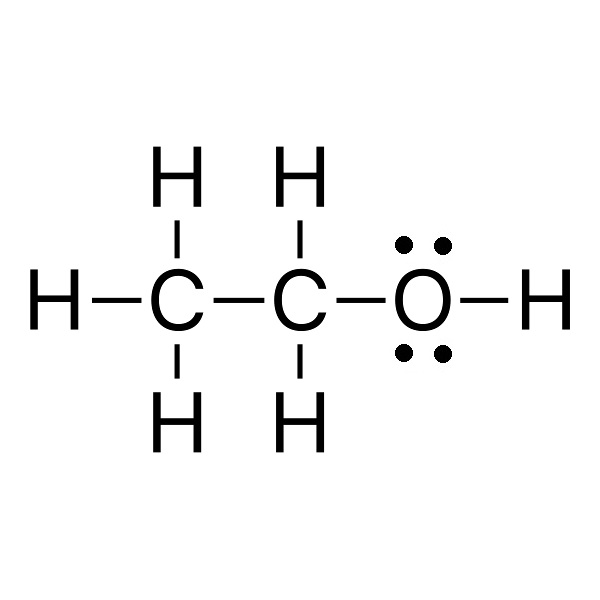 |
A (44.1 g/mol) |
B (46.1 g/mol) |
C (46.1 g/mol) |
 |
 |
 |
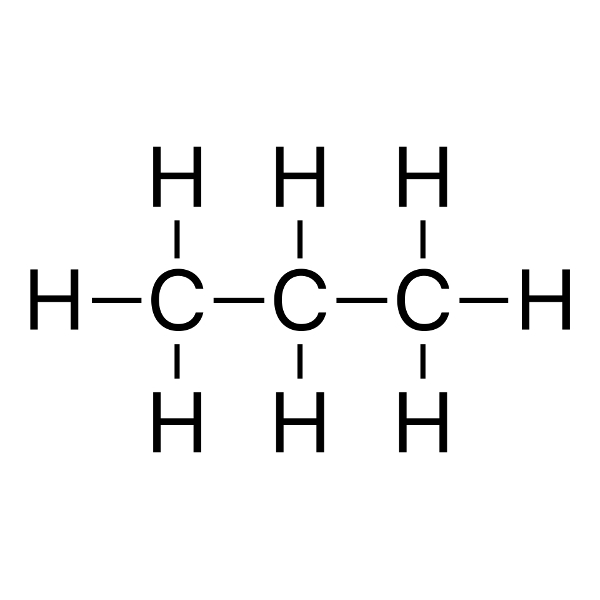
propane Tb = -42 °C |
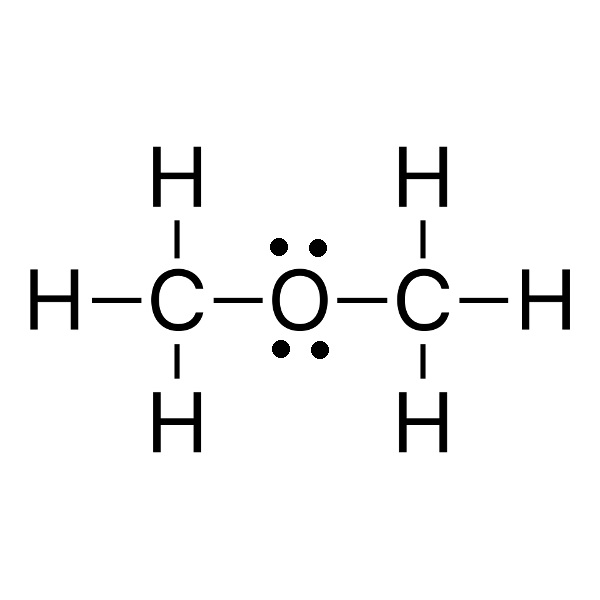
dimethyl ether Tb = -23 °C |
|
 |
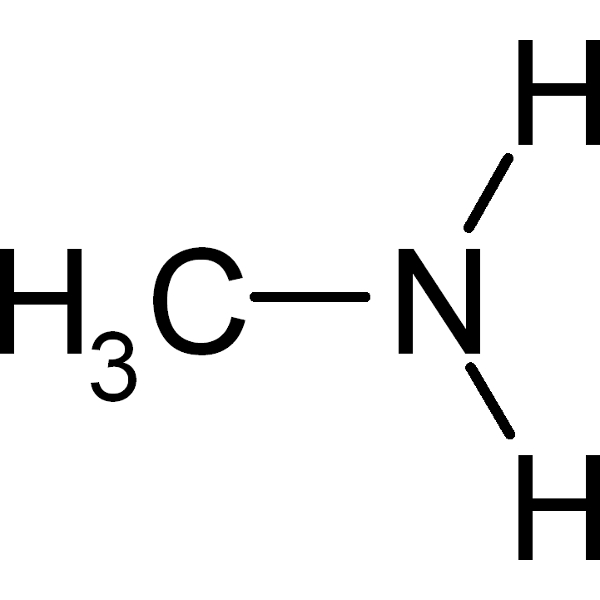 |
31 g/mol |
34 g/mol |
 |
 |
Tf = −138 °C |
Tf = −93 °C |
|
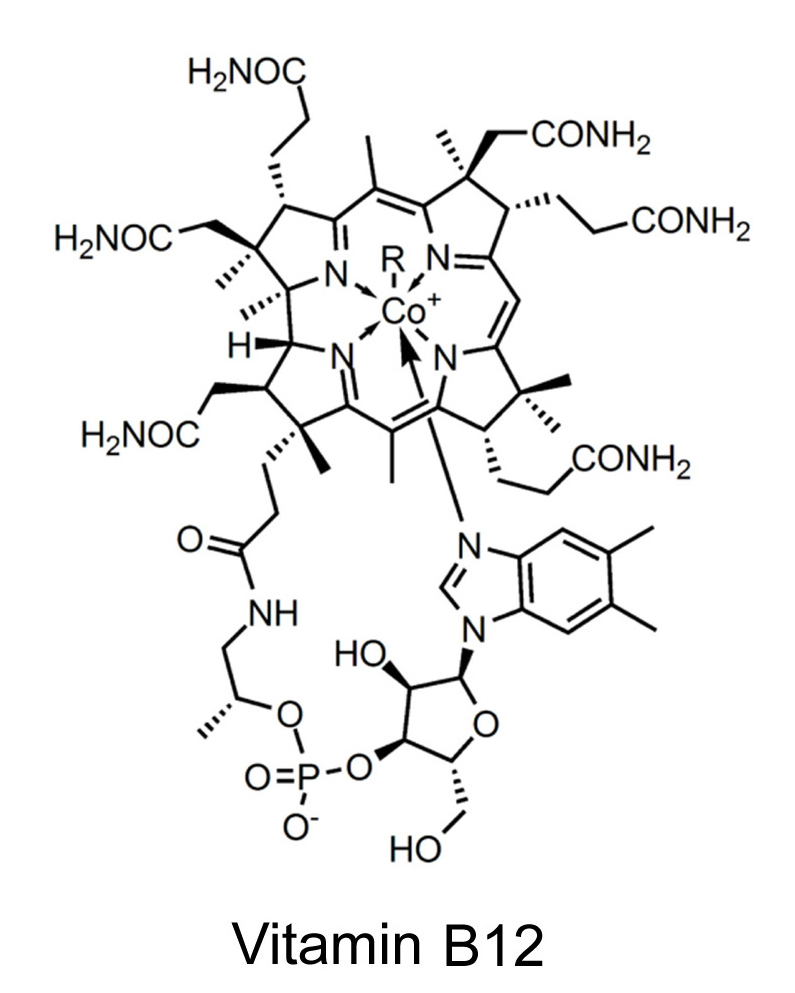
|
|